DIY: Zero Waste and Vegan Ice Cream
Posted by Pawan Saunya on1.6 million edible bananas are thrown away each year in Britain- often because they get too ripe for people to eat. Luckily, you can easily avert these bananas from the waste stream by freezing them. Freezing these overly ripe bananas gives you a sweet, creamy addition to your smoothies, or a perfect base for vegan ice cream.
Dairy ice cream uses ingredients like milk, cream, and eggs for the base. These ingredients are all water, land, and resource-intensive compared to plant-based ingredients, and have a higher carbon footprint.
Dairy ice cream also has ingredients like sugar, chocolate, vanilla, and sometimes palm oil. Palm oil is a notably unsustainable ingredient because it drives deforestation in the Amazon, which increases forest fires and carbon emissions.
Buying vegan ice cream will ensure you steer clear from resource-intensive dairy, but it won’t necessarily ensure that you steer clear from palm oil or other potentially impactful ingredients. The best thing you can do to ensure your vegan ice cream is low impact (and package free) is to make it yourself.
To make your vegan ice cream, use frozen bananas and non-dairy milk instead of dairy and eggs. This way, you’re averting bananas from being tossed in the landfill, and you’re indulging in a treat that has a lower impact than traditional ice cream. Plus, it tastes great.
All you have to do is blend together bananas and non-dairy milk until smooth, and then combine the mixture with ice cream toppings of your choice and stick it in the freezer. You’ll have vegan ice cream in no time.

Maddie Vos
is in charge of maintaining the Zero Waste Club community through regular video content. A keen videographer, she wants to spread the message of sustainability to the masses. She currently is living and working in London, and enjoys yoga and art in her free time.

Kayla Guilliams
is the blog manager for Zero Waste Club, combining her love for writing with her passion for all things environmental sustainability. She is currently a student at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill where she is studying journalism, environmental studies, and food studies in hopes of building a career in environmental activism. You can find her on Instagram as @kaylaguilliams.
5 Apps to Help You Live More Sustainably
Posted by Pawan Saunya onTrying to live a sustainable lifestyle can be daunting because of all the swaps it entails. However, we live in a time where we have apps, websites, and technology that makes everything a little easier- including sustainability. Here are 5 apps that can help you in your efforts to live more sustainably.
Good On You
Clothing is infamous for being both environmentally and socially unsustainable. However, because of a lack of transparency from brands, it can be hard to know what brands act ethically and sustainably. This is where the app Good On You comes in. Good On You allows you to look up a brand and see their sustainability ranking. These rankings are based on their labor, wages, worker safety, resource use and disposal, carbon emissions, and use of animal products among other metrics of social and environmental responsibility. Good On You gets this information by aggregating data from several different certification programs. By breaking down the sustainability of brands into straightforward rankings, Good On You makes information regarding social and environmental responsibility more accessible, making it easier for you to buy from ethical and sustainable clothing brands.

Ecosia
If you’re like every other person with a phone, you probably constantly use Google to access recipes, news, etc.. Ecosia is a search engine like Google, except they use the money they make from ad revenue to plant trees. They plant trees as part of ongoing projects in 15 different countries. They try to plant in biodiversity hotspots to help the local ecosystem, and in areas where planting trees will create value in the land for the local farmers and community members. Just by using Ecosia instead of Google, you’re supporting environmental and social sustainability efforts- it’s probably the easiest sustainable swap you can make.

Happy Cow
Happy Cow is an app that connects you to the vegan and vegetarian restaurants in your area, making it easy to access plant-based meals while on the go. This is especially helpful if you’re in a town where you’re not familiar with the local food scene. Since eating more plant-based meals is a large part of living sustainably, this app is a great resource to help guide you to some of the best plant-based foods in your area. When looking at restaurants on Happy Cow, try to pick local restaurants that appear to have low-waste dining options rather than chain restaurants that typically package everything in plastic.

Too Good To Go
Food waste is a large contributor to carbon emissions, and restaurants are often a large producer of it. Luckily, there are a lot of apps being developed that match this wasted food with those who need it- including Too Good To Go. Too Good To Go allows you to rescue food that would have otherwise gone to waste from local stores at a discounted rate . Not only does this save you money, but it also helps you save the planet.

CoGo
You vote with your dollars every time you make a purchase, so it’s important to know what values the businesses you’re supporting hold. CoGo is an app that makes voting with your dollars easy by connecting you with local businesses that hold your same values. You tell the app what values matter most to you- veganism, carbon-neutral practices, waste reduction, etc.- and CoGo will tell you what businesses in your area also hold these values. Not only will this help you shop more sustainably and ethically, but it’s also a way to let businesses know what sustainability practices you value most.


Sara Benitez
Sara is a traveling yoga teacher with a love for animals and adventures in nature. She has a passion for helping make the world a kinder place through mindfulness practices. She currently lives and works between Spain and London, where she runs group and private classes as well as annual retreats. You can find her on Instagram as @yogawithsara
Photo by @shanicreates
How You Can Help Stop Climate Change
Posted by Pawan Saunya onThe climate crisis is well underway. Some scientists argue that the warming of the planet has reached a point beyond return, and the full impact that we will see from this crisis has been underestimated. Reversing the damage that has been caused by human activity, if even possible, will require unprecedented effort and coordination from governments, businesses, citizens and scientists. Many people are unaware of the impact that individual actions can have on the environment, and would prefer someone else to do something about it- namely their government. As is currently visible around the globe, the government won’t solve the problem of climate change, at least not without pressure from the public. It is normal to feel powerless, inundated daily with bad news of worsening carbon levels, biodiversity loss, melting ice, floods, forest fires, plastic oceans… the list goes on. Preventing these disasters from exacerbating requires radical transformations in the transportation, energy, industrial, commercial and agricultural sectors. As a citizen and a consumer there are two ways in which you can take action:
1. Every time you spend money you are casting a vote for the kind of world you want
2. If you are fortunate to live in a democracy, you can vote to have a say as to what your country is doing for climate change
In addition to pushing for systematic change, there is a lot that you can do at your own will. It might not be possible to do everything at once, but over time you can integrate many of the following practices as part of your daily life:

Energy
Reducing your energy consumption can reduce your carbon footprint. You can save energy by:
· Using energy-efficient lighting
· Switching to energy-efficient appliances
· Better insulating your home
· Using renewable energy such as solar, or geothermal technologies
· Switching to green electricity when choosing your electricity supplier.

Transportation
Transportation-related emissions make up a huge chunk of worldwide emissions. Depending on what is available to you and feasible, you can decrease your transportation-related footprint by:
· Walking or riding a bike
· Car sharing
· Using public transport
· Buying an electric vehicle if you need your own car
· Avoiding air travel, which is by far the most polluting mode of transport.

Food
Animal agriculture is a huge source of greenhouse gases. Raising animals for food is highly un-efficient, unsustainable and damaging. Thus, drastically lowering the amount of animal products you eat or eliminating them from your diet completely is one of the single biggest ways that you can help mitigate climate change. Switching to plant based sources of protein instead of meat and incorporating more local and seasonal produce into your diet is not only is better for your health, but better for the earth. Food waste also contributes a lot to emissions, so plan your shopping in advance so that you don’t buy more than you need to. To ensure nothing goes to waste, freeze leftovers, unused vegetables and bread at the end of the week for later use.

Refuse, reduce, reuse, recycle and rot (“The Five R’s of Zero Waste Living”)
Make simple zero waste swaps such as keeping a reusable water bottle and coffee cup on hand for daily use, have an extra bag with you to carry shopping, use cloth towels instead of paper, and wash and reuse containers, boxes, and jars for storage. Together, these drastically reduce the amount of waste that you end up sending to landfill, which can help lower carbon emissions.

Talk about it!
Many fail to recognize the urgency and gravity of the crisis in which we are living, and others simply ignore the crisis altogether. By bringing up the subject to the people around you, it raises greater awareness and concern. This, in turn, leads to motivation and encouragement towards individual actions for progressive change. Taking part in marches, peaceful protests and activism around the cause has the possibility of developing government policy that matches the scale of the challenges we face.

It can be overwhelming to tackle an issue of this magnitude. It’s hard to know which sources to trust, where to start, and it gets you to wonder if we really need to do something if no one else (like the government) seems to give a crap. The ideology of consumerism blinds us to the real drivers of destruction- government and big corporations- and traps us within a narrow circle of decision making. We need to utilize the power that we do have as individuals. As more people affirm their customer power by supporting sustainable businesses, significant changes can occur. Of course, the real drivers of destruction must be addressed, but this will require systemic and structural changes. Nevertheless, fundamental changes in personal behavior are urgently needed. Begin with the small, simple steps outlined above and eventually, it will lead us to more far-reaching and environmentally significant changes. You can’t do everything, but you can do something.

Salomé Savary
Is working as an intern for Zero Waste Club, writing blog posts on all things zero waste, from cooking tips to travelling hacks. She is passionate about encouraging others to adopt low waste habits in any and every aspect of their lives.
What is Renewable Energy?
Posted by Pawan Saunya onOur energy system is a big contributor to the climate crisis. According to the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions, energy accounted for 72% of global manmade emissions in 2013, and a large proportion of these emissions comes from the electricity and heat we use to power our homes.
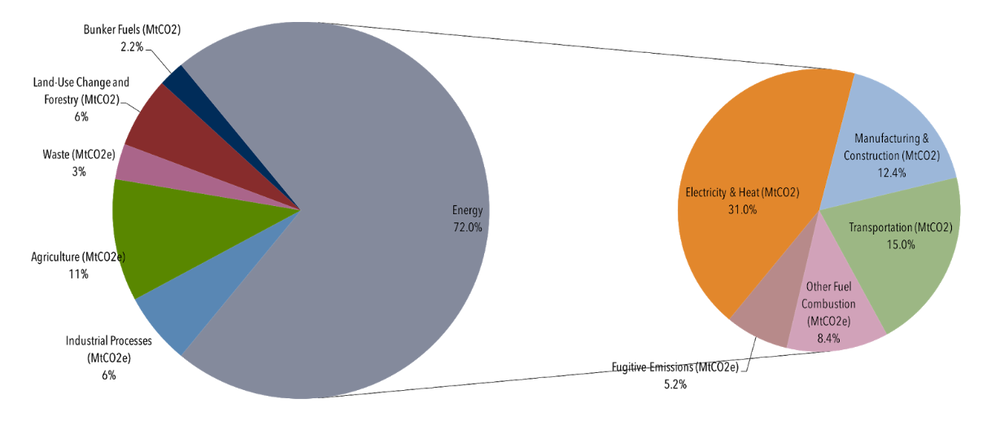
Energy is such a huge source of emissions because our current system relies on the extraction and burning of coal, oil, and gas. Using these resources as the basis of our energy system isn’t just bad because of the large amount of carbon that is released when we burn them, it’s also bad because we will inevitably run out of these resources, and because the process of extracting these resources causes water pollution, air pollution, and habitat destruction.
Relying on this system will only become more problematic as our population grows, increasing our demand for energy. The US Energy Information Administration (EIA) predicts that worldwide energy demand will increase by 50% by 2050. Luckily, there’s an eco-friendly, cost-effective alternative: renewable energy.
Renewable energy is expected to grow alongside our population and energy demand. The EIA predicts that by 2050, renewable energy will be our predominant source of energy.
Renewable energy is a pretty straightforward concept- instead of relying on non-renewable resources like coal, oil, and gas for our energy, we rely on renewable resources like wind, water, and sunlight. Because they’re renewable, there is no fear of us running out. In addition, unlike coal, oil, and gas, these resources have very low rates of greenhouse gas emissions
Renewable energy accounts for 15% of current energy production worldwide. Hydropower is the most popular source of renewable energy, followed by nuclear, wind, and solar energy.
HYDROPOWER:
Hydropower harnesses the energy that is within moving water. Electricity is created by collecting water in a reservoir, controlling the output of the water from this reservoir with a dam (or a series of canals), and then using this water to turn a turbine that generates electricity. The water within this reservoir can be reused.
Hydropower results in very little pollution or emissions, aside from when the infrastructure is built. The construction of this infrastructure can cause pollution, and the infrastructure itself can disrupt habitats and fish migration patterns if not done with the environment in mind.
Hydropower accounts for around 17% of worldwide electricity production, and there is potential for growth into areas in Latin America, Africa, India and China. The main barriers in using hydropower are the money, time and construction required to build the reservoirs and upstart the system.

NUCLEAR:
The creation of nuclear energy requires splitting a uranium atom through a process called nuclear fission. This process releases a lot of energy that is then harnessed in nuclear power plants, resulting in a steady stream of energy. These power plants have low levels of emissions, create a lot of power, and are relatively inexpensive once they’re up and running
The downsides of nuclear energy include the high cost of plant construction and the fact the plants create radioactive waste that has to be carefully disposed of. In addition, there is always the potential for nuclear disasters as a result of an accident or terrorist attack, although the chances of this are slim.
Nuclear energy is often considered to be renewable because of the low levels of emissions, but many argue that it shouldn’t be considered renewable because the amount of uranium that we have on earth is finite. Others argue that the amount of uranium we have available is so large that it shouldn’t matter.

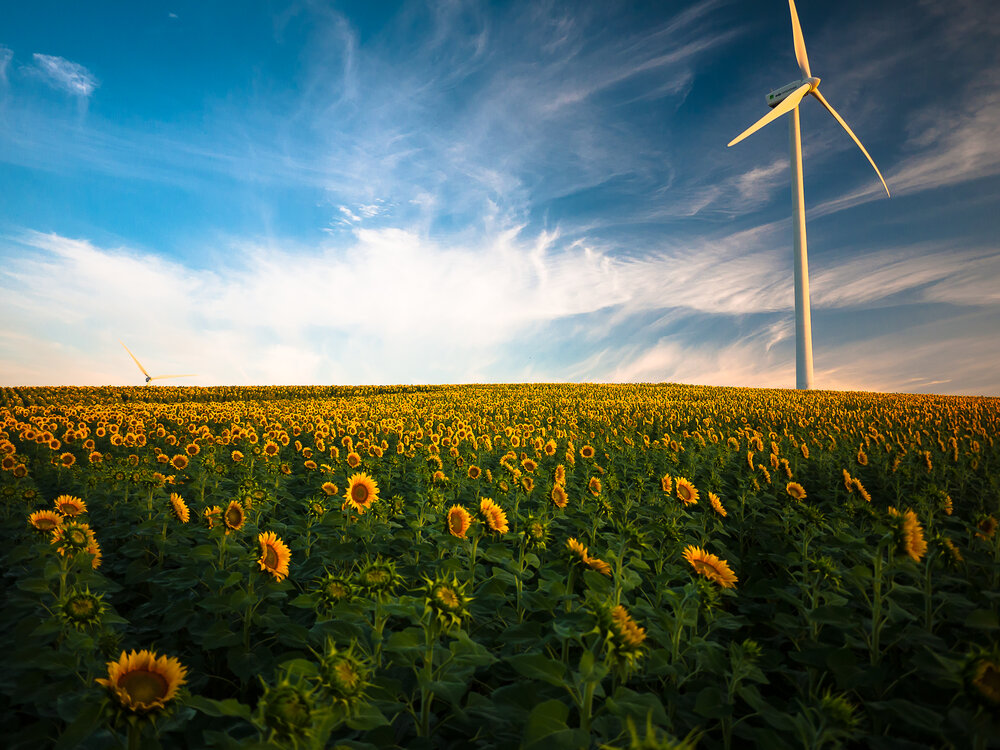
WIND:
Electricity is created from wind through the use of wind turbines. These turbines spin as the wind blows, creating mechanical energy that then spins a generator to produce electricity. These turbines can be large or small and can be located on land or offshore. This process of electricity generation results in very few emissions, is cost-effective and can be built on existing farms and ranches.
There are very few downsides and challenges to using wind power as long as the turbines are installed in the proper locations to avoid harming wildlife and disturbing local communities. The main challenge in using wind power is garnering the public desire to install the turbines, instead of using the land for alternative purposes.
There is also concern that because the presence and strength of wind is variable, that wind turbines won’t provide a consistent source of energy. There are ways to store excess wind power generated for later use, which solves this issue of intermittency. However, the technology for this energy storage is still being developed to be applied on a large scale.

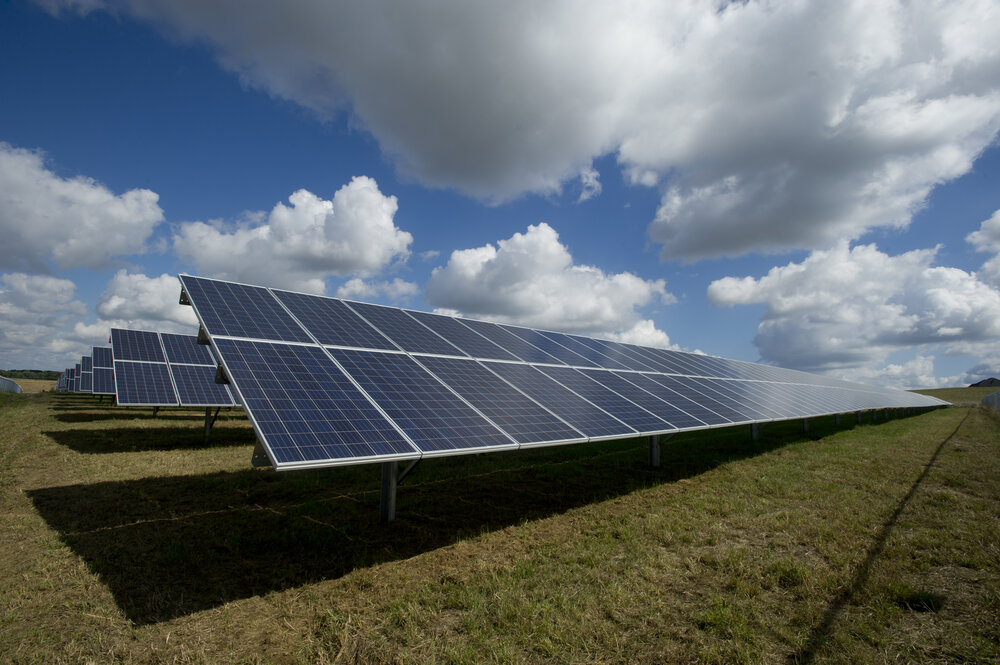
SOLAR:
Solar energy is created by using solar panels to capture the sun's energy and then turn it into electricity. These solar panels are made out of silicon solar cells.
Solar panels are sustainable because of their low rates of emissions and their use of the sun, a renewable source of energy, rather than fossil fuels or oil. Solar panels can also allow homes to be independent and self-sufficient energy producers, as the panels can be installed on rooftops. The price of solar is also rapidly declining as it becomes more popular.
The drawback of solar is its issue with energy storage. Currently, most panels are poor at storing the energy is harnesses for the sun, meaning they only produce energy when the sun is actually shining. This becomes an issue on cloudy and stormy days. However, a lot of development and research is being done to develop the technology of solar batteries that will allow the panels to store energy, so this will no longer be an issue in the near future. There is also some concern about the environmental impacts of creating and disposing of a solar panel.

All of these renewable energy sources have their pros and cons, but the important thing to remember is that they’re all better in the long run than our current energy system. Transforming our energy system to run on renewables like these rather than oil, gas, and coal will drastically reduce rates of greenhouse gas emissions, and could even result in job creation and economic development.

Kayla Guilliams
Is the blog manager for Zero Waste Club, combining her love for writing with her passion for all things environmental sustainability. She is currently a student at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill where she is studying journalism, environmental studies, and food studies in hopes of building a career in environmental activism. You can find her on Instagram as @kaylaguilliams.
5 Ways to Repurpose Food Waste
Posted by Pawan Saunya onIt’s no secret that food waste is a huge issue around the globe. Roughly ⅓ of annual global food production goes to waste, and if food waste was a country, it would be the third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases behind the U.S. and China. These emissions account for the emissions created from growing and processing the waste food, as well as the methane that the food releases when it sits in a landfill. Luckily, food waste is an issue that consumers can play a big role in curbing. Meal planning, freezing surplus produce, buying single bananas and composting food scraps are all effective ways to reduce food waste and cut related emissions. There are also ways to repurpose your food waste into valuable beauty, cleaning, and food products. Here are our top five ways to repurpose your food waste at home.
Donate it
According to the NRDC, ⅔ of the food we throw away is potentially edible. This is because a large amount of food waste stems from consumers overbuying and overpreparing, leaving them with too much food to eat. If this ever happens to you, donate your excess food to your local food bank, or create a free pantry in your neighborhood to give back to your community. If you have extra funds, go to the grocery store and buy up food that is on the brink of going bad, and take it to a food bank or put it in your free pantry. Just make sure the food is 100% edible before donating.

Use citrus peels in cleaners
If you’re looking to live a more eco-friendly life, you’re probably going to want to make your own cleaners. Traditional household cleaners are chocked full of toxic ingredients and are packaged in plastic. To make your own, combine your citrus peel scraps with ⅔ cup of white vinegar and let it infuse for at least a week. Then, put one part citrus-vinegar and one part water in a spray bottle, and use it as you would a normal house cleaner. This is a great way to repurpose your citrus peels, and a great way to avoid using toxic cleaners.

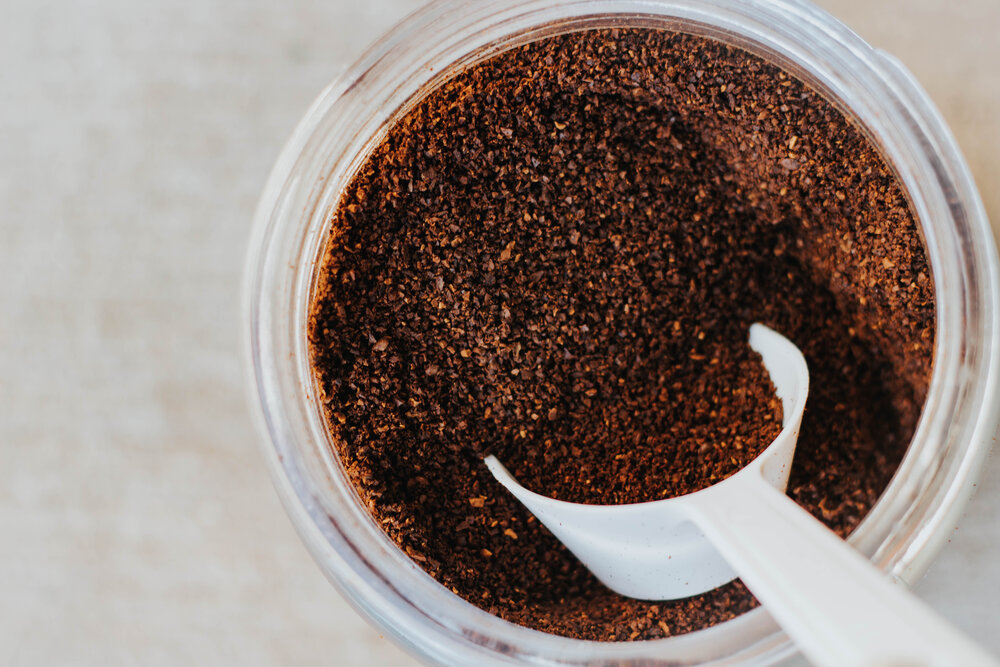
Use coffee grounds in exfoliating scrubs
If you drink coffee every day, your morning ritual probably consists of throwing away coffee grounds. If you’re like me, you store them in a mason jar in your fridge, because coffee grounds feel too expensive to throw away. Lucky for me, these coffee grounds don’t just sit in my fridge with no use- there are a ton of ways to repurpose the grounds into valuable goods. My favorite? An exfoliating scrub. Exfoliating scrubs can be relatively expensive, so making my own with a waste product I inevitably create is a win-win. All I do is combine two parts coffee grounds and 1 part oil (olive, coconut, or avocado), and then use it in the shower like I would any other scrub. You can also add essential oils or vanilla extract. Don’t use this scrub more than once a week- it could hurt your drain.

Make veggie broth
Vegetable peels, seeds, tops, stems… food waste from vegetables really adds up. But, instead of throwing them away, store them in your freezer and use them to make veggie broth! All you have to do is collect your veggie scraps, and then combine them in a pot with water, garlic, and any other seasonings you see fit. Simmer it, strain it, and voila- you have veggie broth!

Make Croutons
Making croutons is a great use of stale bread or bread that you won’t otherwise eat. All you have to do is cut the bread into cubes, drizzle it with olive oil and seasonings, and bake it. Easy and delicious.

How do you repurpose food waste?

Kayla Guilliams
Is the blog manager for Zero Waste Club, combining her love for writing with her passion for all things environmental sustainability. She is currently a student at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill where she is studying journalism, environmental studies, and food studies in hopes of building a career in environmental activism. You can find her on Instagram as @kaylaguilliams.
